Page 37 - New Cloth Market December 2022 Digital Edition
P. 37
Industrial Hemp Fibers: An Overview
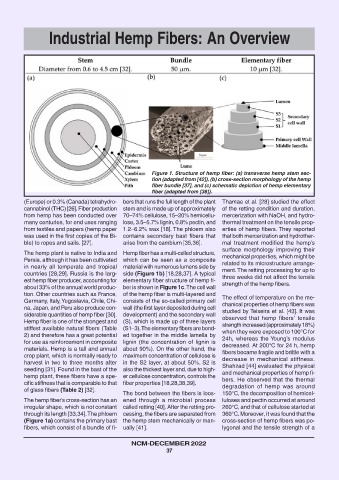
Figure 1. Structure of hemp fiber: (a) transverse hemp stem sec-
tion (adapted from [42]), (b) cross-section morphology of the hemp
fiber bundle [37], and (c) schematic depiction of hemp elementary
fiber (adapted from [38]).
(Europe) or 0.3% (Canada) tetrahydro- bers that runs the full length of the plant Thamae et al. [28] studied the effect
cannabinol (THC) [26]. Fiber production stem and is made up of approximately of the retting condition and duration,
from hemp has been conducted over 70–74% cellulose, 15–20% hemicellu- mercerization with NaOH, and hydro-
many centuries, for end uses ranging lose, 3.5–5.7% lignin, 0.8% pectin, and thermal treatment on the tensile prop-
from textiles and papers (hemp paper 1.2–6.2% wax [18]. The phloem also erties of hemp fibers. They reported
was used in the first copies of the Bi- contains secondary bast fibers that that both mercerization and hydrother-
ble) to ropes and sails. [27]. arise from the cambium [35,36]. mal treatment modified the hemp’s
surface morphology improving their
The hemp plant is native to India and Hemp fiber has a multi-celled structure,
mechanical properties, which might be
Persia, although it has been cultivated which can be seen as a composite
related to its microstructure arrange-
in nearly all temperate and tropical material with numerous lumens side by
ment. The retting processing for up to
countries [28,29]. Russia is the larg- side (Figure 1b) [18,28,37]. A typical
three weeks did not affect the tensile
est hemp fiber producer, accounting for elementary fiber structure of hemp fi-
strength of the hemp fibers.
about 33% of the annual world produc- ber is shown in Figure 1c. The cell wall
tion. Other countries such as France, of the hemp fiber is multi-layered and
The effect of temperature on the me-
Germany, Italy, Yugoslavia, Chile, Chi- consists of the so-called primary cell
chanical properties of hemp fibers was
na, Japan, and Peru also produce con- wall (the first layer deposited during cell
studied by Teixeira et al. [43]. It was
siderable quantities of hemp fiber [30]. development) and the secondary wall
observed that hemp fibers’ tensile
Hemp fiber is one of the strongest and (S), which is made up of three layers
strength increased (approximately 18%)
stiffest available natural fibers (Table (S1–3). The elementary fibers are bond-
when they were exposed to 100°C for
2) and therefore has a great potential ed together in the middle lamella by
24h, whereas the Young’s modulus
for use as reinforcement in composite lignin (the concentration of lignin is
decreased. At 200°C for 24 h, hemp
materials. Hemp is a tall and annual about 90%). On the other hand, the
fibers became fragile and brittle with a
crop plant, which is normally ready to maximum concentration of cellulose is
decrease in mechanical stiffness.
harvest in two to three months after in the S2 layer, at about 50%. S2 is
Shahzad [44] evaluated the physical
seeding [31]. Found in the bast of the also the thickest layer and, due to high-
and mechanical properties of hemp fi-
hemp plant, these fibers have a spe- er cellulose concentration, controls the
bers. He observed that the thermal
cific stiffness that is comparable to that fiber properties [18,28,38,39].
degradation of hemp was around
of glass fibers (Table 2) [32].
The bond between the fibers is loos- 150°C, the decomposition of hemicel-
The hemp fiber’s cross-section has an ened through a microbial process luloses and pectin occurred at around
irregular shape, which is not constant called retting [40]. After the retting pro- 260°C, and that of cellulose started at
through its length [33,34]. The phloem cessing, the fibers are separated from 360°C. Moreover, it was found that the
(Figure 1a) contains the primary bast the hemp stem mechanically or man- cross-section of hemp fibers was po-
fibers, which consist of a bundle of fi- ually [41]. lygonal and the tensile strength of a
NCM-DECEMBER 2022
37