Page 49 - New Cloth Market November 2022 Digital Edition
P. 49
Chitosan-Based Sustainable Textile Technology: Process, Mechanism, Innovation & Safety
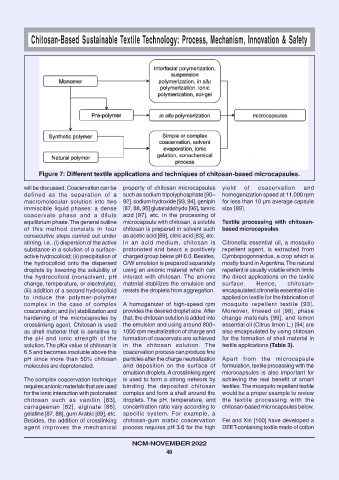
Figure 7: Different textile applications and techniques of chitosan-based microcapsules.
will be discussed. Coacervation can be property of chitosan microcapsules yield of coacervation and
defined as the separation of a such as sodium tripolyphosphate [90– homogenization speed at 11,000 rpm
macromolecular solution into two 92], sodium hydroxide [93, 94], genipin for less than 10 µm average capsule
immiscible liquid phases: a dense [87, 88, 95] glutaraldehyde [96], tannic size [89].
coacervate phase and a dilute acid [97], etc. In the processing of
equilibrium phase. The general outline microcapsule with chitosan, a soluble Textile processing with chitosan-
of this method consists in four chitosan is prepared in solvent such based microcapsules
consecutive steps carried out under as acetic acid [89], citric acid [83], etc.
stirring, i.e., (i) dispersion of the active In an acid medium, chitosan is Citronella essential oil, a mosquito
substance in a solution of a surface- protonated and bears a positively repellent agent, is extracted from
active hydrocolloid; (ii) precipitation of charged group below pH 6.0. Besides, Cymbopogonnardus, a crop which is
the hydrocolloid onto the dispersed O/W emulsion is prepared separately mostly found in Argentina. The natural
droplets by lowering the solubility of using an anionic material which can repellent is usually volatile which limits
the hydrocolloid (nonsolvent, pH interact with chitosan. The anionic the direct applications on the textile
change, temperature, or electrolyte); material stabilizes the emulsion and surface. Hence, chitosan-
(iii) addition of a second hydrocolloid resists the droplets from aggregation. encapsulated citronella essential oil is
to induce the polymer-polymer applied on textile for the fabrication of
complex in the case of complex A homogenizer of high-speed rpm mosquito repellent textile [93].
coacervation; and (iv) stabilization and provides the desired droplet size. After Moreover, linseed oil [98], phase
hardening of the microcapsules by that, the chitosan solution is added into change materials [99], and lemon
crosslinking agent. Chitosan is used the emulsion and using around 800– essential oil (Citrus limon L.) [94] are
as shell material that is sensitive to 1000 rpm neutralization of charge and also encapsulated by using chitosan
the pH and ionic strength of the formation of coacervate are achieved for the formation of shell material in
solution. The pKa value of chitosan is in the chitosan solution. The textile applications (Table 3).
6.5 and becomes insoluble above this coacervation process can produce fine
pH since more than 50% chitosan particles after the charge neutralization Apart from the microcapsule
molecules are deprotonated. and deposition on the surface of formulation, textile processing with the
emulsion droplets. A crosslinking agent microcapsules is also important for
The complex coacervation technique is used to form a strong network by achieving the real benefit of smart
requires anionic materials that are used binding the deposited chitosan textiles. The mosquito repellent textile
for the ionic interaction with protonated complex and form a shell around the would be a proper example to review
chitosan such as vanillin [83], droplets. The pH, temperature, and the textile processing with the
carrageenan [82], alginate [86], concentration ratio vary according to chitosan-based microcapsules below.
gelatine [87, 88], gum Arabic [89], etc. specific system. For example, a
Besides, the addition of crosslinking chitosan-gum arabic coacervation Fei and Xin [100] have developed a
agent improves the mechanical process requires pH 3.6 for the high DEET-containing textile made of cotton
NCM-NOVEMBER 2022
49