Page 39 - New Cloth Market November 2022 Digital Edition
P. 39
Chitosan-Based Sustainable Textile Technology: Process, Mechanism, Innovation & Safety
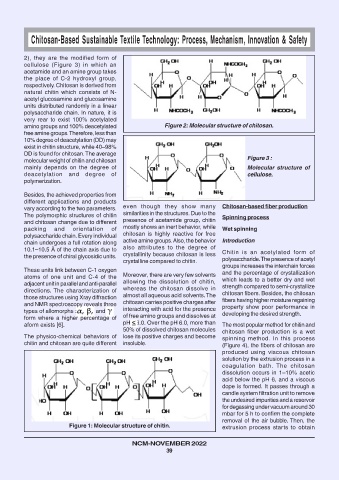
2), they are the modified form of
cellulose (Figure 3) in which an
acetamide and an amine group takes
the place of C-2 hydroxyl group,
respectively. Chitosan is derived from
natural chitin which consists of N-
acetyl glucosamine and glucosamine
units distributed randomly in a linear
polysaccharide chain. In nature, it is
very rear to exist 100% acetylated
amino groups and 100% deacetylated Figure 2: Molecular structure of chitosan.
free amine groups. Therefore, less than
10% degree of deacetylation (DD) may
exist in chitin structure, while 40–98%
DD is found for chitosan. The average
molecular weight of chitin and chitosan Figure 3 :
mainly depends on the degree of Molecular structure of
deacetylation and degree of cellulose.
polymerization.
Besides, the achieved properties from
different applications and products
even though they show many Chitosan-based fiber production
vary according to the two parameters.
similarities in the structures. Due to the
The polymorphic structures of chitin Spinning process
presence of acetamide group, chitin
and chitosan change due to different
mostly shows an inert behavior, while
packing and orientation of Wet spinning
chitosan is highly reactive for free
polysaccharide chain. Every individual
active amine groups. Also, the behavior Introduction
chain undergoes a full rotation along
also attributes to the degree of
10.1–10.5 Å of the chain axis due to
crystallinity because chitosan is less Chitin is an acetylated form of
the presence of chiral glycosidic units.
crystalline compared to chitin. polysaccharide. The presence of acetyl
groups increases the interchain forces
These units link between C-1 oxygen
Moreover, there are very few solvents and the percentage of crystallization
atoms of one unit and C-4 of the
allowing the dissolution of chitin, which leads to a better dry and wet
adjacent unit in parallel and anti-parallel
whereas the chitosan dissolve in strength compared to semi-crystallize
directions. The characterization of
almost all aqueous acid solvents. The chitosan fibers. Besides, the chitosan
those structures using Xray diffraction
chitosan carries positive charges after fibers having higher moisture regaining
and NMR spectroscopy reveals three
interacting with acid for the presence property show poor performance in
types of allomorphs : and
of free amino groups and dissolves at developing the desired strength.
form where a higher percentage of
pH 6.0. Over the pH 6.0, more than
aform exists [6]. The most popular method for chitin and
50% of dissolved chitosan molecules
chitosan fiber production is a wet
The physico-chemical behaviors of lose its positive charges and become
spinning method. In this process
chitin and chitosan are quite different insoluble.
(Figure 4), the fibers of chitosan are
produced using viscous chitosan
solution by the extrusion process in a
coagulation bath. The chitosan
dissolution occurs in 1–10% acetic
acid below the pH 6, and a viscous
dope is formed. It passes through a
candle system filtration unit to remove
the undesired impurities and a reservoir
for degassing under vacuum around 30
mbar for 5 h to confirm the complete
removal of the air bubble. Then, the
Figure 1: Molecular structure of chitin. extrusion process starts to obtain
NCM-NOVEMBER 2022
39