Page 15 - New Cloth Market November 2022 Digital Edition
P. 15
The Use of Enzymes in the Textile Chemical Formulating Industry (TCF)
Introduction
AGES
The use of enzymes in the textile value chain (Figure 1) is gaining global recognition because of their eco-
friendly characteristics. The enzyme technology is attractive because enzymes are highly specific and
efficient, and work under mild conditions. Furthermore, the use of enzymes results in reduced process
times, energy and water savings and improved product quality.
Generally, enzymes do not possess any health-related adverse effects except for the fact that they can
induce respiratory allergy. Therefore, a two-part guidance document series was developed on safe han-
dling of enzymes in the textile value chain, i.e. how to avoid the formation of airborne dust and aerosols,
which if inhaled in sufficiently high amounts can lead to respiratory allergy. This issue of the guidance
document series focuses on the textile chemical formulating industry (TCF) (Figure 1).
EXECUTIVE P
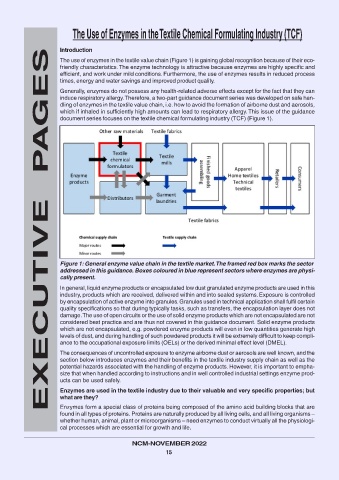
Figure 1: General enzyme value chain in the textile market. The framed red box marks the sector
addressed in this guidance. Boxes coloured in blue represent sectors where enzymes are physi-
cally present.
In general, liquid enzyme products or encapsulated low dust granulated enzyme products are used in this
industry, products which are received, delivered within and into sealed systems. Exposure is controlled
by encapsulation of active enzyme into granules. Granules used in technical application shall fulfil certain
quality specifications so that during typically tasks, such as transfers, the encapsulation layer does not
damage. The use of open circuits or the use of solid enzyme products which are not encapsulated are not
considered best practice and are thus not covered in this guidance document. Solid enzyme products
which are not encapsulated, e.g. powdered enzyme products will even in low quantities generate high
levels of dust, and during handling of such powdered products it will be extremely difficult to keep compli-
ance to the occupational exposure limits (OELs) or the derived minimal effect level (DMEL).
The consequences of uncontrolled exposure to enzyme airborne dust or aerosols are well known, and the
section below introduces enzymes and their benefits in the textile industry supply chain as well as the
potential hazards associated with the handling of enzyme products. However, it is important to empha-
size that when handled according to instructions and in well controlled industrial settings enzyme prod-
ucts can be used safely.
Enzymes are used in the textile industry due to their valuable and very specific properties; but
what are they?
Enzymes form a special class of proteins being composed of the amino acid building blocks that are
found in all types of proteins. Proteins are naturally produced by all living cells, and all living organisms –
whether human, animal, plant or microorganisms – need enzymes to conduct virtually all the physiologi-
cal processes which are essential for growth and life.
NCM-NOVEMBER 2022
15