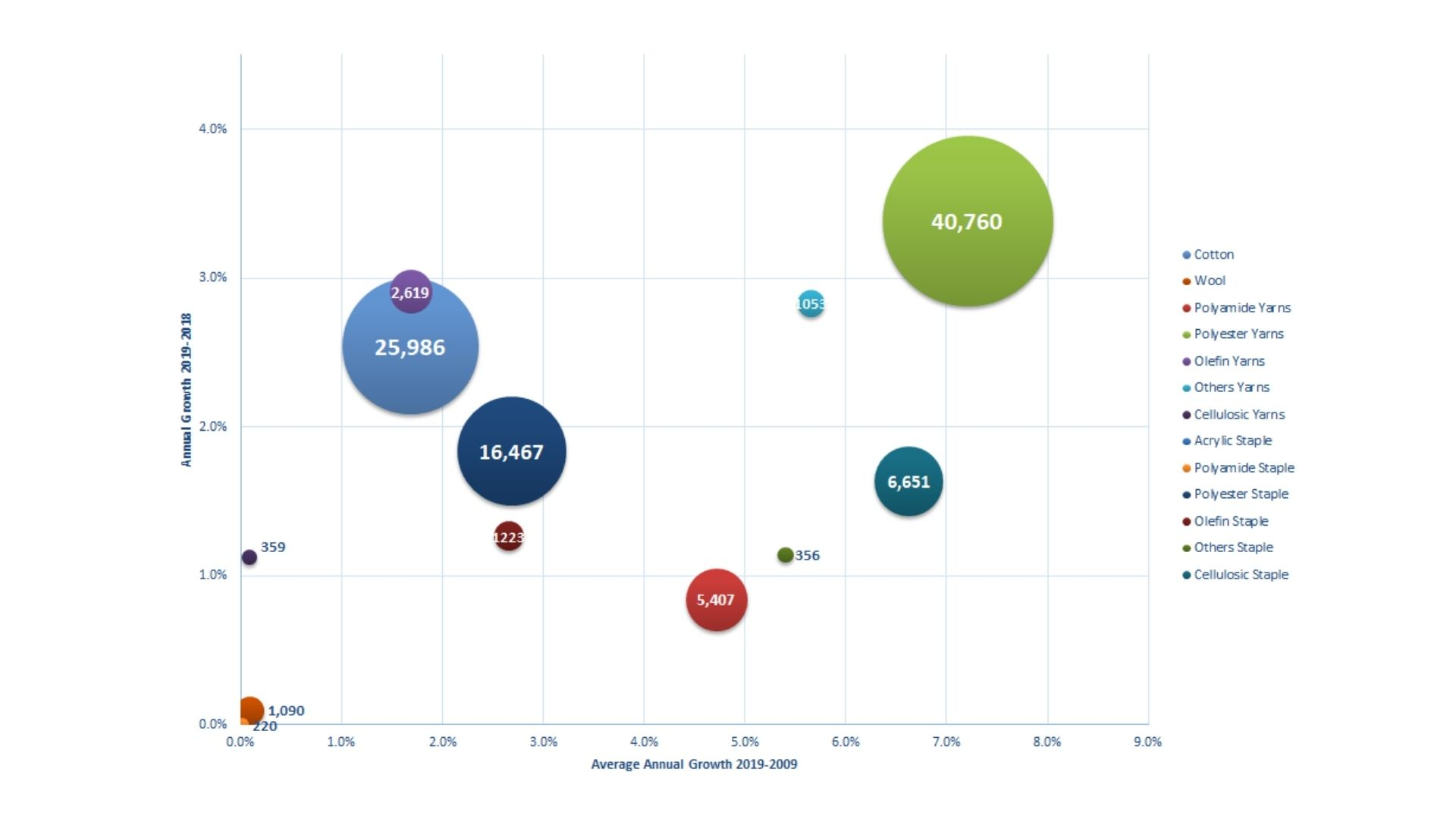
World Production of Cotton, Wool and Man-Made Fibres
Man-made fibres account for 75% of all fibres produced worldwide, and for circa 80% in Europe, including Turkey. World production was 76.5 million tonnes in 2019. European production was 4.6 million tonnes.
Their principal end-use is in clothing, carpets, household textiles and a wide range of technical products – tyres, conveyor belts, fillings for sleeping bags and cold-weather clothing, filters for improving the quality of air and water in the environment, fire-resistant materials, reinforcement in composites used for advanced aircraft production, and much else. Fibres are precisely engineered to give the right combination of qualities required for the end-use in question: appearance, handle, strength, durability, stretch, stability, warmth, protection, easy care, breathability, moisture absorption and value for money, for example. In many cases, they are used in blends with natural fibres such as cotton and wool.
Man-made fibres come in two main forms: continuous filament, used mainly for weaving, knitting or carpet production; and staple, discontinuous lengths of fibre which can be spun into yarn or incorporated in unspun uses such as fillings or nonwovens.
Man-made fibres are classified into three classes, those made from natural polymers, those made from synthetic polymers and those made from inorganic materials.
Fibres from Natural Polymers
The most common natural polymer fibre is viscose, which is made from the polymer cellulose obtained mostly from farmed trees. Other cellulose-based fibres are Lyocell, Modal, Acetate and Triacetate.
Less common natural polymer fibres are made from rubber, alginic acid and regenerated protein.
Fibres from Synthetic Polymers
There are very many synthetic fibres i.e. organic fibres based in principle on petrochemicals (bio-based polymers are being increasingly used). The most common are polyester, polyamide (often called nylon), acrylic and modacrylic, polypropylene, polyethylene, the segmented polyurethanes which are elastic fibres known as elastanes (or spandex in the USA), and speciality high-tenacity fibres such as the high performance aramids and UHMwPE (Ultra High Molecular weight PolyEthylene).
Fibres from Inorganic Materials
The inorganic man-made fibres are fibres made from materials such as glass, metal, carbon or ceramic. These fibres are very often used to reinforce plastics to form composites.
MMF range includes: Viscose, Modal, Lyocell, Acetate, Acrylic, Polyamide, Polyester, Aramid, Elastane, UHMwPE, Polyolefins, Carbon, Glass etc.
The European man-made fibres (MMF) industry has been active on circularity for many years. It is a frontrunner in MMF in this respect worldwide but also inside the European textile value chain.in order to reach a full circular economy in fibres and textiles we need:
- Efficient waste collection and handling system
- Technology for separating and recycling fibres
- Global responsibility
- Imported textiles and end-of-life materials
- Biodegradable MMF
- Interface with REACH regulations
- Standardization and harmonization
- Eco-design
- Mutual collaboration
- R&D and more…





