
How linen is made into fabrics? (Picture for illustration purpose: Courtesy sewguide.com)
The textile industry not only promises to enhance our production capabilities but also aims to uplift rural economies and promote sustainable practices. An innovative technology development for spinning linen yarn from linseed fiber, has been published in the International Journal of Advanced Biochemistry Research.
The Importance of Linseed
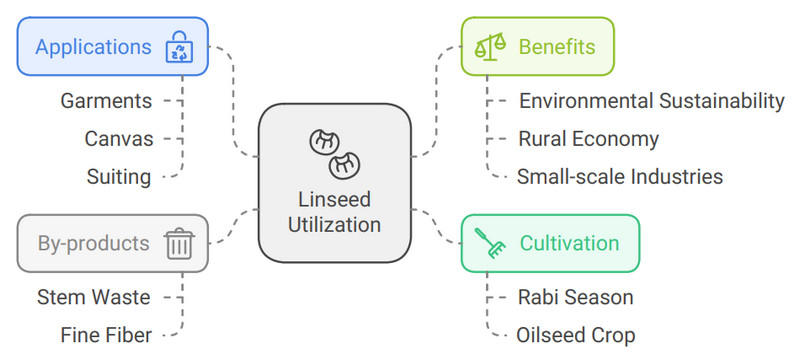
Linseed, or Linum usitatissimum, is a critical oilseed crop primarily cultivated in the rabi season. Each hectare of linseed can produce between 15 to 20 quintals of stem waste, which contains 15 to 20% fine fiber suitable for extraction. This waste, often overlooked, can be transformed into high-quality linen, which is not only valuable for garments but also for various industrial applications, including canvas and suiting. By utilizing this resource, we can significantly contribute to environmental sustainability while enhancing the rural economy through small-scale industries.
 The Fiber Extraction Process
The Fiber Extraction Process
The process of extracting fibers from linseed involves a meticulous method of rotting away the woody stem and internal pith, which binds the fibers together. While the linseed plant is relatively easy to grow, the extraction process remains labor-intensive and is often performed manually to preserve the delicate fibers. This presents both a challenge and an opportunity for innovation.
Technological Innovations
To address these challenges, the researchers have developed a Motorized Charkha and an Upgraded Rotor Spinning Machine. These advancements significantly enhance the efficiency of spinning linseed fibers into yarn. For instance, while traditional methods yield only 250-300 grams of yarn per day, the upgraded rotor spinning technology can produce up to 12 kilograms per day. This not only increases productivity but also improves the quality and fineness of the yarn produced.
Moreover, the upgraded rotor spinning system is eco-friendly, requiring no fossil fuels and minimizing environmental risks. This aligns perfectly with our commitment to sustainable practices and the empowerment of local communities.
Economic and Social Impact
The introduction of these technologies is not just about increasing production; it is about empowering individuals, particularly women, who have traditionally engaged in spinning as a means of livelihood. The motorized charkha was initially designed to enhance the income of less privileged women by enabling them to produce and sell handmade garments. By modernizing this tool, we are not only preserving a cultural heritage but also providing a pathway for economic independence.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the development of linen yarn from linseed fiber represents a significant step forward in both textile technology and rural economic development. By harnessing the potential of linseed waste, we can create high-quality products while promoting sustainable practices and empowering local communities.
 The Fiber Extraction Process
The Fiber Extraction Process




